Brief Intro on Radiant Heater, Convection Heater and Fan Heater
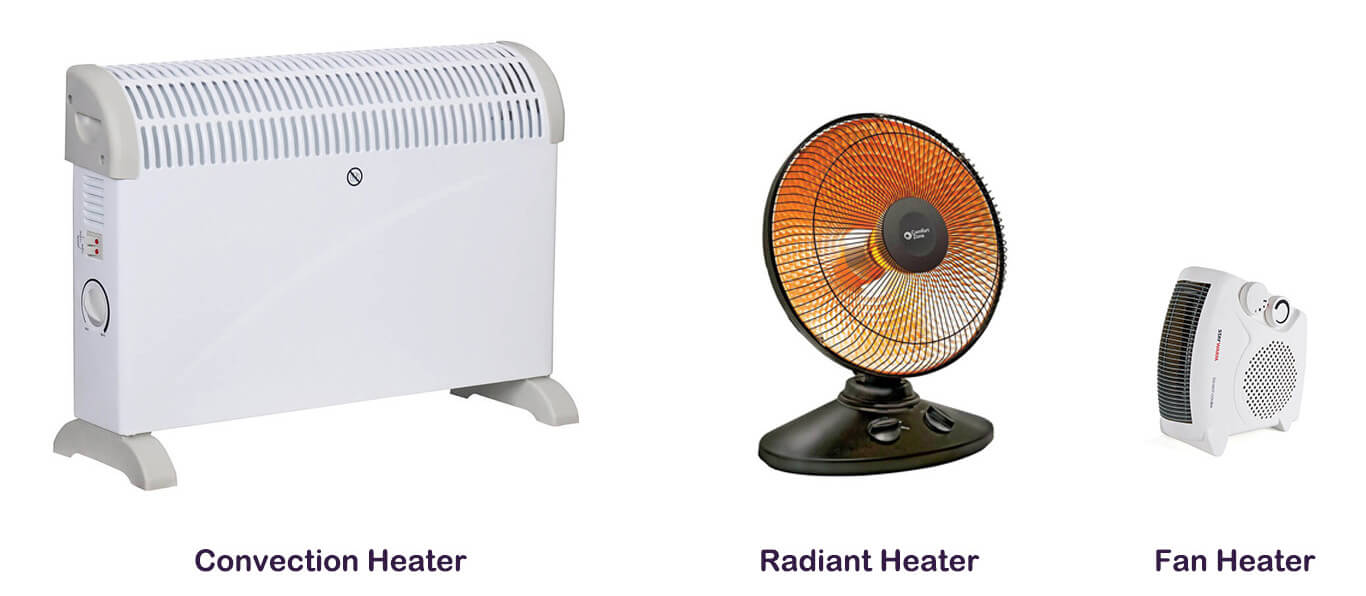
Radiant Heater
Electric radiant heating uses heating elements that reach a high temperature. The element is usually packaged inside a glass envelope resembling a light bulb and with a reflector to direct the energy output away from the body of the heater. The element emits infrared radiation that travels through air or space until it hits an absorbing surface, where it is partially converted to heat and partially reflected. This heat directly warms people and objects in the room, rather than warming the air. This style of heater is particularly useful in areas through which unheated air flows. They are also ideal for basements and garages where spot heating is desired. More generally, they are an excellent choice for task-specific heating.
Radiant heaters operate silently and present the greatest potential danger of ignition of nearby furnishings due to the focused intensity of their output and lack of overheat protection. In the United Kingdom, these appliances are sometimes called electric fires, because they were originally used to replace open fires.
The active medium of the heater depicted in this section is a coil of nichrome resistance wire inside a fused silica tube, open to the atmosphere at the ends, although models exist where the fused silica is sealed at the ends and the resistance alloy is not nichrome.
Convection Heater
In a convection heater, the heating element heats the air in contact with it by thermal conduction. Hot air is less dense than cool air, so it rises due to buoyancy, allowing more cool air to flow in to take its place. This sets up a convection current of hot air that rises from the heater, heats up the surrounding space, cools and then repeats the cycle. These heaters are sometimes filled with oil or thermal fluid. They are ideally suited for heating a closed space. They operate silently and have a lower risk of ignition hazard if they make unintended contact with furnishings compared to radiant electric heaters.
Fan Heater
A fan heater, also called a forced convection heater, is a kind of convection heater that includes an electric fan to speed up the airflow. They operate with considerable noise caused by the fan. They have a moderate risk of ignition hazard if they make unintended contact with furnishings. Their advantage is that they are more compact than heaters that use natural convection and are also cost-efficient for portable and small room heating systems.


